Introduction:
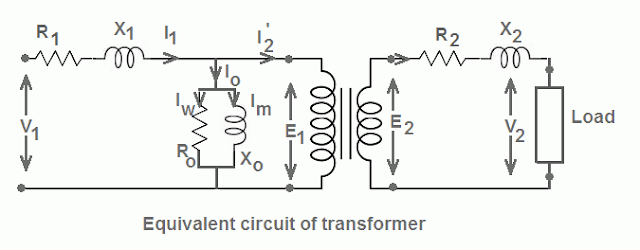
The approximate equivalent circuit of a transformer is given in the following figure. The various parameters of this circuit can be determined by open circuit and short circuit test. Various performance characteristics (such as regulation, efficiency) can be determined with the help of this circuit without actually loading the transformer. This experiment is designed to perform the open circuit and short circuit test. Obtained results will be compared with those from theoretical calculations.
Objective:
01. The purpose of a short circuit test is to determine the series branch parameters of the equivalent circuit of a Real transformer.
02. The open circuit test, or "no-load test" is one of the methods used in electrical engineering to determine the no-load impedance in the excitation branch of a transformer.
Apparatus:
(1) Power Supply .
(2) AC Voltmeter (0-250V)
(3) AC Ammeter (0-1.5A)
(4) Single Phase wattmeter.
Working Procedure:
(1) Open Circuit Test: Complete connections as shown in the experimental setup. Apply rated voltage to across the terminal 1 and terminal 2 of the transformer. Note the readings of the ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter.
(2) Short Circuit Test: Complete connections as shown in the experimental setup. Gradually apply voltage across the terminal 1 and terminal 2 of the transformer unit rated current flows through the ammeter. Quickly take the readings of the ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter.
Data:
Nameplate data of the transformer:
Data table for short circuit test:
Data table for open circuit test:
Calculations:
- Core loss, W = W watt
- Core loss resistance (referred to the HT side)
- Magnetizing resistance (referred to HT side)
- Copper loss,
- Equivalent resistance,
- Equivalent resistance
Report:
- What are the approximations of the short and the open circuit tests?
Answer: 2. Why open circuit test is performed in the high tension side whereas short circuit test is performed in the low tension side?
Answer:
The open circuit test is always performed on the low-voltage side of the transformer. Because, if it is performed on the high voltage side, the no-load current I0 would be inconveniently small and the applied voltage would be inconveniently large.
3. Draw the exact and approximate equivalent circuit of a transformer. Define all the parameters.
4. Draw the vector diagram of a real transformer for resistive, inductive and capacitive load.
Answer:
Discussion:
By experiment we can test open circuit and short circuit of a transformer. From this experiment we get to know how the efficiency and regulation of the transformer can be calculated from an equivelent circuit.








0 Comments